10 Essential Tips for Efficient Belt Conveyor System Maintenance and Optimization
Effective maintenance and optimization of a belt conveyor system are crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of any industrial process that relies on material handling. Belt conveyors serve as the backbone of various manufacturing and distribution facilities, transporting materials swiftly and efficiently from one point to another. However, the demands of continuous operation can take a toll on these systems. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the life of the equipment but also enhances its performance, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs.
In this guide, we present ten essential tips that encompass best practices for maintaining and optimizing your belt conveyor system. These strategies are designed to address common issues that may arise during operation and to provide actionable insights for improving system efficiency. By adhering to these tips, operators can ensure that their belt conveyors operate at peak performance, thereby maximizing productivity and minimizing disruptions. Whether you are new to belt conveyor systems or looking to refine your existing practices, this outline will serve as a valuable resource in your pursuit of operational excellence.
Understanding the Basics of Belt Conveyor Systems
Belt conveyor systems are vital components in various industries, facilitating the efficient transport of materials across diverse environments. Understanding the basic elements of these systems is essential for ensuring optimal performance. At their core, belt conveyor systems consist of a continuous loop of material—the conveyor belt—supported by a series of pulleys and rollers. This design allows for smooth movement and minimizes friction, enabling the transport of heavy loads over considerable distances.
Key components of a belt conveyor system include the drive pulley, which powers the belt, and the idler pulleys, which help to maintain tension and support the belt’s weight. Additionally, the belt material, often composed of rubber or fabric, is selected based on the specific materials being transported and the operational environment. Proper alignment of these components is crucial, as misalignment can lead to increased wear and tear, reduced efficiency, and potential operational failures. Understanding these fundamentals not only aids in maintenance practices but also informs optimization strategies to enhance throughput and prolong the lifespan of the conveyor system.
10 Essential Tips for Efficient Belt Conveyor System Maintenance and Optimization
This bar chart illustrates the importance of various maintenance practices for belt conveyor systems, measured by their impact on performance efficiency. Each category represents a different maintenance tip with an associated effectiveness rating on a scale of 1 to 10.
Identifying Common Maintenance Issues in Belt Conveyors
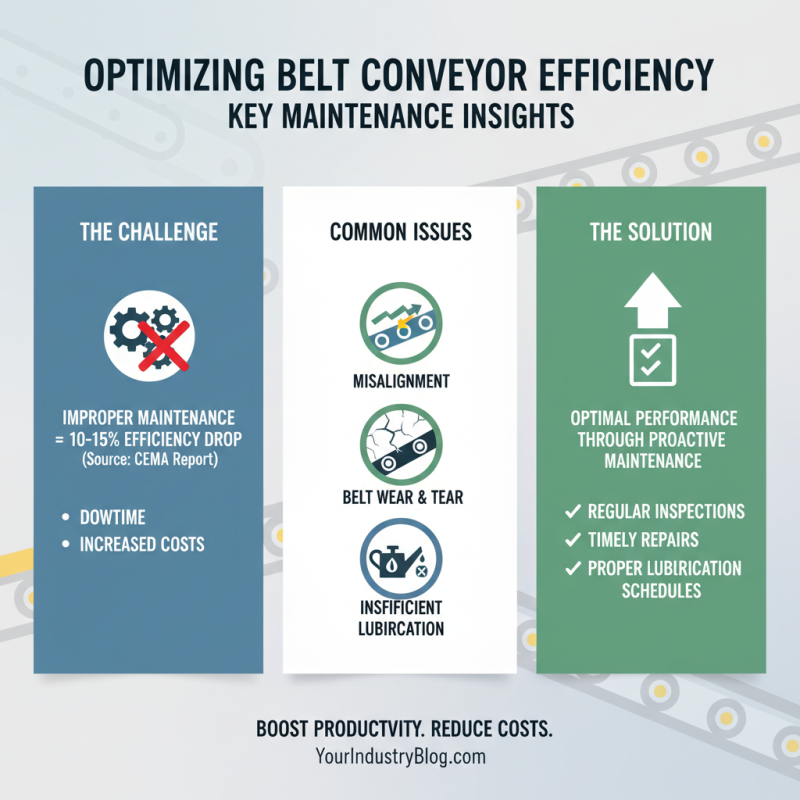
Belt conveyors are crucial in various industries for material handling, but their efficiency can be hampered by common maintenance issues. According to a report by the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA), improper maintenance practices can lead to a 10-15% decrease in system efficiency. Identifying and addressing these issues is essential for optimal performance. Common problems include misalignment, wear and tear of belts, and insufficient lubrication, which can cause downtime and increase operational costs.
To mitigate these issues, regular inspections and proactive maintenance are key. One tip is to implement a scheduled maintenance program that allows operators to check for belt wear and alignment regularly. Additionally, utilizing infrared thermography can help identify hotspots in the conveyor system, indicating potential mechanical failures before they become critical. Regular training for maintenance personnel can also enhance skills, helping them spot maintenance issues early.
Another essential tip is ensuring proper belt tensioning. A belt that is either too tight or too loose can lead to excessive wear and ultimately system failure. Monitoring this can prevent costly replacements and downtime, as preliminary findings indicate that maintaining optimal tension can extend belt life by up to 30%. With these strategies, facilities can significantly improve their conveyor system efficiency while minimizing maintenance-related disruptions.
Implementing Regular Inspection and Maintenance Schedules
Implementing a regular inspection and maintenance schedule is crucial for the optimal performance of belt conveyor systems. A proactive approach not only minimizes unplanned downtimes but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. Regular inspections should include checking for wear and tear on belts, alignment of components, and the functionality of drive systems. Documenting the condition of each component over time can provide valuable insights into when maintenance or replacement is needed, allowing for timely interventions that prevent more serious issues down the line.
In addition to visual inspections, it's essential to incorporate routine maintenance tasks, such as lubrication of bearings and cleaning of pulleys. Creating a checklist for these tasks can help ensure that nothing is overlooked during maintenance sessions. Furthermore, training personnel on best practices and the importance of these routines fosters a culture of accountability and safety within the team. By committing to an organized maintenance schedule, businesses can achieve significant cost savings and enhanced operational efficiency, ensuring that their belt conveyor systems function smoothly and reliably.
Optimizing Conveyor Belt Performance through Proper Tensioning Techniques
Proper tensioning techniques are crucial for optimizing the performance of belt conveyor systems. Ensuring that the conveyor belt maintains the right level of tension not only enhances its operational efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. If the belt is too loose, it may slip, leading to uneven material flow and increased wear on various components. Conversely, excessive tension can strain the motor and other drive elements, resulting in premature failure. Regular monitoring and adjustment of tension are essential practices that operators should incorporate into their maintenance routines.
To achieve optimal tensioning, it is important to consider the specific characteristics of the conveyor system and the materials being transported. Implementing a systematic approach to tension adjustments, such as following manufacturer guidelines or utilizing tension measurement tools, can guide operators in achieving the desired settings. Additionally, environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity, can affect belt performance and may necessitate periodic re-evaluation of tension levels. By prioritizing proper tensioning techniques, businesses can enhance overall conveyor belt efficiency, reduce downtime, and minimize maintenance costs, ultimately leading to improved operational productivity.
Upgrading Technology for Enhanced Conveyor Efficiency and Safety
Upgrading technology in belt conveyor systems can significantly enhance efficiency and safety across various industries. Embracing automation through advanced monitoring systems allows for real-time data analysis, enabling operators to make informed decisions swiftly. For example, integrating sensors that track belt alignment and speed can prevent potential mishaps, thus reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance tools powered by artificial intelligence can alert personnel to component wear before it leads to failure, ensuring seamless operations and an overall safer work environment.
Additionally, incorporating energy-efficient drives and motors can optimize power consumption, contributing to both cost savings and environmental sustainability. Smart software solutions can adjust the conveyor speed according to the flow of materials, minimizing energy waste and maximizing throughput. By aligning maintenance schedules with these technological upgrades, facilities can bolster their operational capabilities, leading to enhanced productivity and reduced risk of accidents. Investing in modern technology not only streamlines processes but also establishes a culture of safety, making it a pivotal aspect of conveyor system management.
10 Essential Tips for Efficient Belt Conveyor System Maintenance and Optimization
| Tip Number | Maintenance Tip | Expected Outcome | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regular Belt Alignment Checks | Reduces wear and extends life | Monthly |
| 2 | Clean Conveyor Components | Prevents contamination and increases efficiency | Weekly |
| 3 | Lubricate Moving Parts | Reduces friction and saves energy | Bi-weekly |
| 4 | Inspect for Wear and Tear | Prevents unexpected downtime | Monthly |
| 5 | Monitor Belt Tension | Ensures proper operation and minimizes slippage | Weekly |
| 6 | Utilize Technology for Monitoring | Real-time data for better decision-making | Ongoing |
| 7 | Review Load Capacity Regularly | Prevents overloading and improves safety | Quarterly |
| 8 | Train Staff on Safety Protocols | Enhances safety and reduces accidents | Annually |
| 9 | Upgrade Technology as Needed | Improves efficiency and reliability | As Required |
| 10 | Create a Maintenance Schedule | Ensures regular upkeep and optimized performance | Ongoing |
Related Posts
-

Top Packaging Equipment Trends You Need to Know for Your Business
-

Exploring the Future of Conveyor Systems in Automation and Smart Manufacturing
-

Why Your Business Needs an Industrial Packing Machine for Efficiency and Growth
-

2025 Top Filling Machine Innovations Enhancing Efficiency and Precision in Manufacturing
-

Revolutionizing Packaging: How Automatic Bagging Machines Enhance Efficiency and Precision in Industries
-
2025 How to Choose the Right Conveyor Parts for Your Business Needs
